Safe Food Handling Practices
130 likes | 244 Views
Learn about cross-contamination, cleaning vs. sanitizing, insect and rodent control, waste management, HACCP, and health inspection guidelines to ensure food safety in your establishment.

Safe Food Handling Practices
E N D
Presentation Transcript
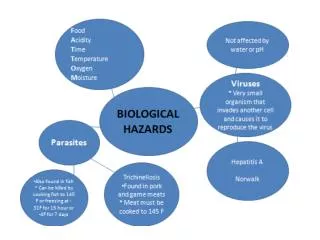
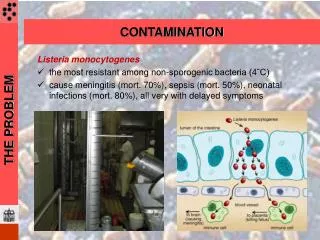
Cross Contamination • Occurs when microorganisms transfer from one product to another by hand, utensils, equipment, or other physical contact • The largest cause of foodborne illnesses • Result of human negligence • Always clean and sanitize hands, cutting boards, workstations, utensils after each job. Store raw food properly in refrigerator • Chicken on bottom shelf (takes longest to cook) • Use air tight containers to store raw food and clearly label and date • Lowest internal cooking temperature is stored on top • Clean vs. Sanitary • Cleaning • Removing visible debris, grease, and grime • First step before sanitizing • Use hot soapy water to clean and/or degreaser • Sanitizing • Two types: heat and chemical • Kills pathogens • Heat • Used with dish machines. Need to reach 171F and 180F to sanitize small equipment • Chemical • Most commonly used • Water hardness, water temperature, residue, detergents are factors that influence effectiveness • Must be changed every 4 hours • Never mix chemicals • Wear gloves • Dilute with water • Allow to air dry ALWAYS
INSECT AND RODENT CONTROL • Spread biological hazards through urine and feces, which contain pathogens • Spread hazards with their feet and bodies by crawling through garbage then over work surfaces • Flies and cockroaches are greatest health risk • Mice and rats are the biggest rodent problem • Must keep kitchen clean and sanitary to prevent issues • Don’t leave food/garbage laying around • Use screens on windows and doors – make sure sealed properly • Use blowers on doors • Check all delivery boxes for insect damage (eggs, droppings) • Seal cracks in foundation, doors, and windows • WASTE CONTROL • Line trash can with heavy duty liners • Empty into dumpster outside of restaurant often • Don’t allow cans to overflow • Recycle • Regularly clean cans and dumpster to prevent insect/rodent issues • Always wash hands after touching garbage
HAZARD ANALYSIS CRITICAL CONTROL POINT • HACCP – identifies where contamination is most likely to occur • Was originally developed for NASA • Tracks PHF (potentially hazardous foods) • CCP – critical control point • Step where control can be applied to prevent or eliminate food safety hazard • Where pathogens are killed • Records should be kept on HACCP foods • THE HEALTH INSPECTOR • Randomly comes to inspect facility, unannounced • Not the enemy – makes sure rules are followed • Frequency determined by restaurant size, prior inspection results, risk level of customer base, workload of health department • Responsible for public safety • Check for biological, chemical, and physical hazards