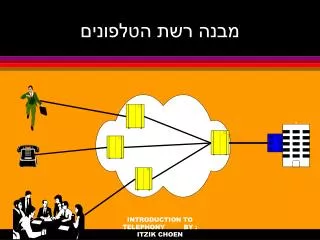
מבנה רשת הטלפונים
230 likes | 402 Views
מבנה רשת הטלפונים. מושגים בסיסיים. PSTN : Public Switched Telephone Network. T1/E1 : Protocol Of Carrying Voice In Frames. POTS : Plane Old Telephone Services. PRI/BRI : Primary/Basic Rate Interface - ISDN. מושגים בסיסיים. Off Hook : When Telephone Handset is up.(open)

מבנה רשת הטלפונים
E N D
Presentation Transcript
מבנה רשת הטלפונים INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
מושגים בסיסיים • PSTN : Public Switched Telephone Network. • T1/E1 : Protocol Of Carrying Voice In Frames. • POTS : Plane Old Telephone Services. • PRI/BRI : Primary/Basic Rate Interface - ISDN. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
מושגים בסיסיים • Off Hook : When Telephone Handset is up.(open) • On Hook : When Telephone Handset is down.(closed) INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
PULSE DIALING INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
TONE DIALING INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
Tone Dialing • Tone dials operate by sending a combination of frequencies that are translate into digits by the central office switch. • It uses 3 x 4 matrix to transmit pairs of frequencies to a tone receiver in the switch. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
Tone Dialing • Each of 12 buttons generates a unique pair of frequencies that are detected and translated into the called number. • For instance : dialing a ‘1’ produces the combined tone of 697 Hertz and 1.2 khertz. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
Tone Dialing • The choice of the frequencies is international, designed to prevent the creation of harmonics or overtones that misinterpreted by detection circuitry. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
Voice Channel Bandwidth INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
TDM : Time Division Multiplexing INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
TDM • TDM is a scheme in which numerous signals are combined for transmission on a single communications line or channel. • Each signal is broken up into many segments, each having very short duration. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
TDM • The circuit that combines signals at the source end of a communications link is known as a multiplexer. • It accept the input from each individual end user, break each signal into segments, and assigns the segments to the composite signal in a rotating, repeating sequence. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
TDM • At the other end of the long-distance cable, the individual signals are separated out by means of a circuit called a demultiplexer, and routed to the proper end users. • T1 - 24 users using TDM. • E1 - 30 users using TDM. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
Digitizing Voice : PCM Waveform Encoding • Nyquist Theorem : sample at twice the highest frequency. • Vice frequency range: 0.3-3.4kh. • Sampling frequency at 8 kHz - every 125 s. • each sample is 8 bit. • 8000hz x 8 bit = 64 KBPS. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
PCM - Pulse Code Modulation • Designed to carry digitized voice, based on AT&T FDM hierarchy. • STEP 1 : Sample analog signal at 8 kHz. • Results: Pulse Amplification Modulation (PAM). INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
PCM - Pulse Code Modulation • STEP 2 : Digitize PAM samples to 13 bits and compress to 8 bits using A-law or -law. • Result : Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
-Law and A -Law INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
-Law and A -Law • In North America: -Law • y=ln(1+ x)/ln(1+ ), =255 • in Europe : A-Law • y=(1+ln Ax)/(1+ln A), A=87.6 • Linear for small values of x and logarithmic for larger values. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
-Law and A -Law • For example : INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
Voice Compression Technologies • Objective : reduce bandwidth consumption. • Compression algorithms are optimized for voice. • Unlike data compression : these are “loose”. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
Differential PCM-DPCM • Based on the relatively slow changes between successive samples. • Fewer bits are required to describe the differential from one sample to the next, than to describe the absolute signal level. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
Adaptive DPCM-ADPCM • To improve the resolution, DPCM contains a predictor that “guesses” the next sample. • The encoder quantizes the difference between the new sample and the predicted new sample. INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN
NEXT LESSON • Voice compression(3 Algorithm) • CELP • CS-ACELP • LD-CELP INTRODUCTION TO TELEPHONY BY : ITZIK CHOEN