Rhetoric
170 likes | 312 Views
Rhetoric. The Art of Using Language to Persuade. How well can you persuade others?. Choose a side of the room depending on whether you agree or disagree with the following statements. Choose a side….

Rhetoric
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Rhetoric The Art of Using Language to Persuade
How well can you persuade others? Choose a side of the room depending on whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Choose a side… Legalized physician-assisted suicide has improved the care of terminally ill patients.
Choose a side… Laws permitting concealed weapons ensure public safety.
Choose a side… Technological innovation must be limited to protect humanity.
Choose a side… Marijuana is dangerous and should not be legalized.
Background • The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) identified three basic kinds of appeals that arguments can make: emotional, ethical, and logical. • Aristotle’s types of appeals can help you break down an argument and thus begin to analyze it.
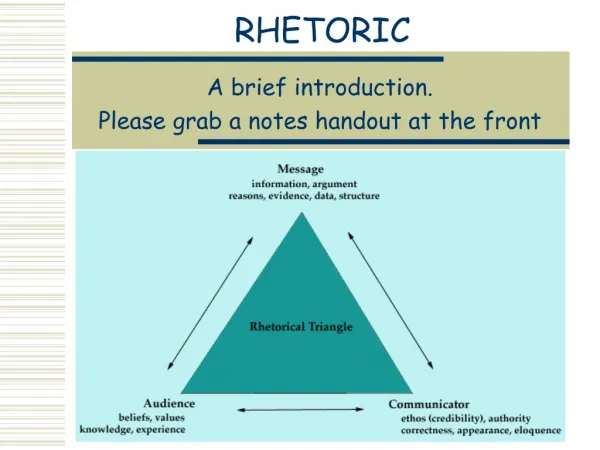
The Rhetorical Triangle Logos (logic, reason) Ethos (ethics, credibility, character) Pathos (feelings, emotion)
ETHOS: Ethical Appeal • “Character” in Greek • Ethical appeals try to convince you by pointing out credibility, moral character, and goodwill of the creator. • In an ethical appeal, the argument’s creator tries to prove that he/she knows the subject well, has a trustworthy character and has the best interests of readers- including YOU- at heart. • Warning: When you recognize that an argument is making an ethical appeal, ask yourself whether the creator successfully demonstrates that he/she actually has the knowledge, trustworthiness, and empathy for the reader that he/she claims to have.
PATHOS: Emotional Appeal • “Suffering” in Greek • Emotional appeals try to convince you by stirring up your feelings and reminding you of your deeply held values. • A visual or verbal text that attempts to evoke laughter, sadness, anger, or fear makes an emotional appeal. • Most arguments include emotional appeals because such appeals make people care about the argument. • CAUTION: Be aware of the difference between appeals that engage your emotions legitimately and appeals that aim to manipulate your feelings.
LOGOS: Logical Appeal • “Word” in Greek • Logical appeals try to convince you by supplying fact-based evidence such as experimental data, observation, testimony, statistics, and personal experience. • Western culture tends to value “facts,” so logical appeals are often viewed as particularly trustworthy. • CUIDADO: But remember, facts can be easily misinterpreted and sources can be unreliable. Thus, even an argument based on apparent facts requires critical investigation.
Choose a side… A federal constitutional amendment is needed to stop gay marriage.
Choose a side… Using animals for medical testing is both ethical and essential.
Choose a side… Media influence on teenage sexuality is significant, and should be further regulated.
Choose a side… Addiction to video gaming is a problem.