Understanding Weathering: Mechanical and Chemical Processes
110 likes | 198 Views
Explore how mechanical and chemical weathering break down rocks, including ice wedging, thermal expansion, biotic factors, oxidation, and carbonation. Learn how these processes form soil and sedimentary rock.

Understanding Weathering: Mechanical and Chemical Processes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Weathering Mechanical and Chemical
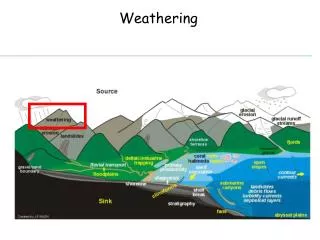
What is Weathering? • First step to forming soil and sedimentary rock • Breakdown of rock into smaller pieces • The smaller pieces do not move to a new location until erosion carries them away • Many types of weathering
What is Mechanical Weathering? • Breakdown of rock into smaller pieces without any change in the chemical composition of its minerals • Sometimes called “physical” weathering • Rock is torn apart by physical force, rather than by chemical breakdown • Smaller pieces do not move to a new location until erosion carries them away
Mechanical - Ice Wedging • Ice Wedging • Water fills joints of rocks and freezes • Water expands 10% when it freezes, pushes rock apart • Repeated freeze and thaw cycles over the years causes rock to break along joint
Mechanical - Exfoliation • Exfoliation or unloading • Rock breaks off into sheets along joints which are parallel to the surface • Caused by expansion of rock due to uplift and removal of surface material that originally buried the rock
Mechanical - Thermal • Thermal expansion • Repeated daily heating and cooling of rock • Heat causes expansion; cooling causes contraction • Different minerals expand and contract at different rates causing the rock to split
Mechanical - Biotic • Biotic – means life • Weathering caused by living organisms • Plant roots act as a wedge and widen cracks • Other causes of biotic weathering are digging animals, microscopic plants and animals, algae and fungi.
What is Chemical Weathering? • Breakdown of rock into smaller pieces because of change in the chemical composition of its minerals • Chemical reactions break down the bonds holding the rocks together, causing them to fall apart • Chemical weathering occurs in all types of rock • Rock reacts with water, gases and solutions
Chemical - Oxidation • Oxidation - oxygen combines with other elements in rocks to form new types of rock • New substances are usually much softer than original, easier for other forces to break rock apart • Causes a “rusting” of the rock, often causes a color change in the rock
Chemical - Carbonation • Carbonation – Carbon dioxide (CO2) is dissolved in water making carbonic acid • Weak acid is formed when CO2 in the air mixes with rain. This is the same acid found in soft drinks. • Acid is too weak to harm plants and animals but slowly causes feldspars and limestone to decompose